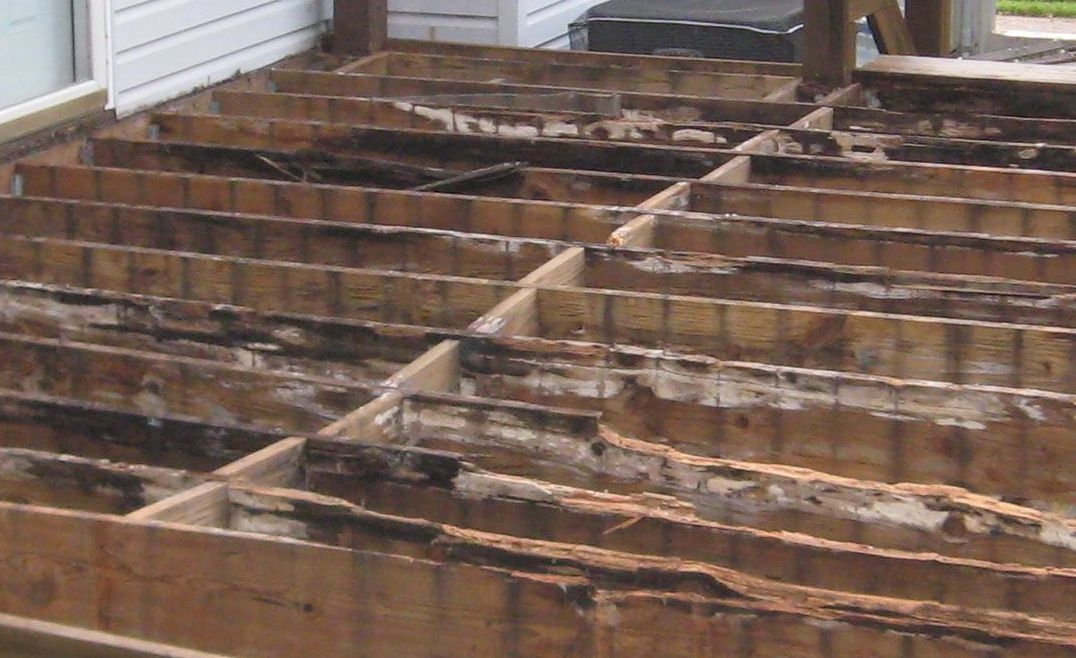
Wooden structure floor are more prone to collapse compared to reinforced concrete structures
Wooden structure floor beams are more prone to collapse compared to reinforced concrete structures due to several key factors. Firstly, when individuals walk, they exert approximately 1.6 kN/sqm of alternating loads on the floor. Let set the same live load is typically 1.9 kN/sqm.

Structure weight
Additionally, the self-weight of a reinforced concrete structure is around 2.4 kN/sqm, whereas a wooden structure only amounts to 0.5 kN/sqm
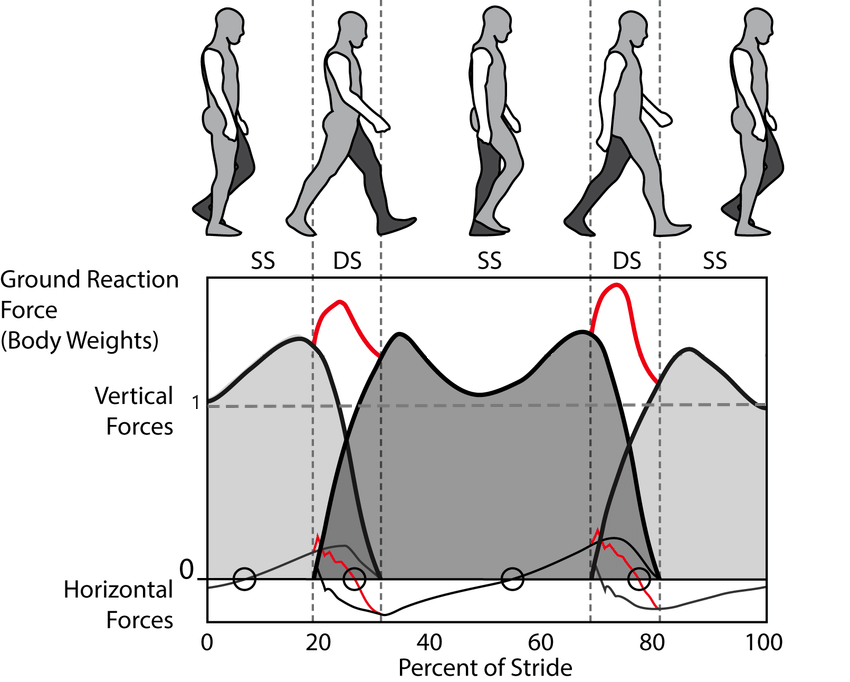
Effects of alternating loads
Considering the total load, the wooden structure amounts to 2.4 kN/sqm. Calculating based on a 50% fatigue limit, the maximum alternating load that wooden structures can withstand without experiencing fatigue is only 1.2 kN/sqm. In contrast, the higher self-weight of a reinforced concrete structure means that the same alternating load is a smaller proportion of the total load, making it less likely to exceed the fatigue limit of the material.
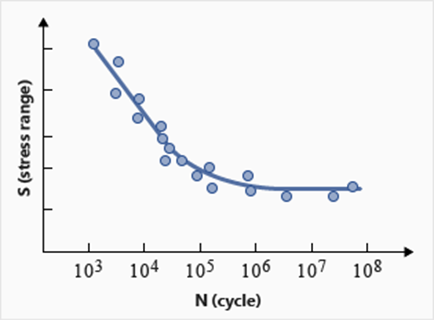
There is no need to worry too much about this situation. It usually occurs after a million cycles, in the main pedestrian areas of houses 35-50 years old, but it will indeed greatly increase the cost of later maintenance.
It’s important to note that this analysis does not suggest that concrete structures are immune to fatigue-induced floor collapses. Rather, in residential design, under light load conditions, concrete structures exhibit better durability. However, in industrial settings such as factories, where heavier loads are common, the same problem occurs with reinforcement concrete structures.